What is Evaporative Cooling
Evaporative cooling uses evaporation to help cool the air. Based on the principles of evaporation, hot and dry outside air is drawn through water-soaked cooling pads. As the air is pushed through these pads, the water evaporates and the heat in the air is absorbed, which lowers the air temperature. A fan pushes the cool air throughout the house via a network of ducts.
The key to effective evaporative cooling is ensuring that each of the cooling pads are completely saturated during operation and that the systems fan and motor are sized and designed to deliver the appropriate airflow for the space. The evaporative cooling air process works by evaporating liquid water into vapor using heat from the air while the energy in the air is maintained.
The heat used to evaporate water into water vapor is called latent heat (hidden heat that cannot be detected with a thermometer) of evaporation. For example, it is the heat from the hot pavement that evaporates the water after a summer rainstorm. As the liquid water changes its state into vapor, it absorbs heat from its surroundings; the energy it absorbs is contained in the molecular structure of the vapors.
Evaporative cooling is only possible because of this natural phenomenon of latent heat. This results in the temperature and the sensible heat (that you can feel or sense) of the air dropping. The moisture vapor is added to the air increases the humidity and the latent heat of the air. An evaporative cooler is a system that cools air through the evaporation of water. Evaporative cooling is different from traditional air conditioning systems, which use chemical vapor compression refrigeration cycles.
Evaporative cooling describes this natural phenomenon, however, there are many other terms that are commonly used with the same meaning including evaporative air conditioning, adiabatic cooling, ducted evaporative cooling, swamp coolers and desert coolers.
Evaporative Cooling BenefitsCooling in the USFrequently Asked QuestionsThe benefits of evaporative air conditioning are plenty, there’s never been a better time to invest in an evaporative air conditioner which is simple to maintain and operate and offers superior product performance.
With energy prices escalating and summers typically involving heat waves, evaporative air conditioning offers a significant and increasing edge on refrigerated cooling, when it comes to energy efficiency, healthier air flow, performance and lifestyle.
Cost-effective to run
Learn more
The first thought that comes to mind when operating an air conditioner is the running cost. With modern and innovative evaporative cooling such as Breezair by Seeley International, you can save you up to 80% on cooling energy bills (1).
Low water usage
Learn more
Evaporative air conditioners use a small amount of water. A Breezair evaporative air conditioner for example, uses around 4 gallons of water per day averaged over a year vs. 4 people in a household taking 7-minute showers which is 67 gallons per day (2).
By checking water saving features in different evaporative coolers, you will find that Breezair by Seeley International offers a superior water distribution system, water quality monitoring and automatic water drainage which results in minimum water usage for maximum cooling power.

Quiet operation
Learn more
In the middle of night, there’s nothing more annoying than the noisy buzz of an air conditioner. Seeley International’s evaporative air conditioners have a reputation for being exceptionally quiet, so you won’t hear a thing as you sleep, particularly the Breezair product line which known for being whisper quiet.
Easy maintenance
Learn more
Regular service by a qualified contractor will ensure your evaporative cooler continues to run at its peak efficiency and maintain low evaporative running costs. Scheduling an evaporative cooling service can be arranged through our approved network of contractors.

Improved indoor air quality with high ventilation
Learn more
When the weather heats up there is nothing worse than being stuck inside breathing stale air for hours on end. Fresh air is a major benefit of evaporative air conditioning, supplying 100% fresh, cool, outside air.
It is important to remember that evaporatively cooled air inside a home is not recirculated, so a door or window is left open for this air to escape, providing a home with a complete change in air roughly every two minutes (3).

Evaporative air conditioners are enviromentally friendly
Learn more
Opting for evaporative air conditioning means that you will not only help the environment, but you will also experience natural, cool, fresh filtered air. Evaporative air conditioners use far less electricity compared to refrigerated systems and therefore minimize the environmental impact.
Evaporative air conditioning systems contain no harmful synthetic refrigerants. Compare this to direct expansion systems which may use potent greenhouse gases like hydro fluorocarbons or chlorofluorocarbons.

Adding moisture to the air
Learn more
Evaporative air conditioning can help to increase the amount of moisture in the air. This is especially beneficial for people living in drier climates who can find it difficult to breathe or experience dry and cracked skin when using refrigerated options.
To understand how evaporative cooling works in different climates zones in the US, it’s good to revisit the principles of evaporative cooling. As water is evaporated, sensible heat from the air is converted to latent heat, reducing the temperature. Two temperatures are important when dealing with evaporative cooling.
This is the temperature that we usually think of as air temperature measured by a regular thermometer exposed to the air stream. Typically, the temperature in the US is measured in degrees Fahrenheit (oF).
Wet bulb temperature
This is the lowest temperature that can be reached by saturating air with water vapor. When considering water evaporating into air, the wet bulb temperature is a measure of the potential for evaporative cooling. The dry and wet bulb temperature can be used to calculate the relative humidity.
Evaporation will take place when the relative humidity is below 100% and the air begins to absorb water. Any given volume of air can hold a certain amount of water vapor and the degree of absorption will depend on its starting temperature and the amount of vapor it is already holding.
The term relative humidity describes how much water is already in the air, relative to the amount it can hold. Air is saturated when it cannot hold anymore water.
Energy is required to change water from liquid to vapor. This energy is obtained in an adiabatic process from the air itself. Air entering an evaporative air cooler gives up sensible heat energy to evaporate water. Through this process, the dry bulb temperature of the air passing through the cooler is lowered.
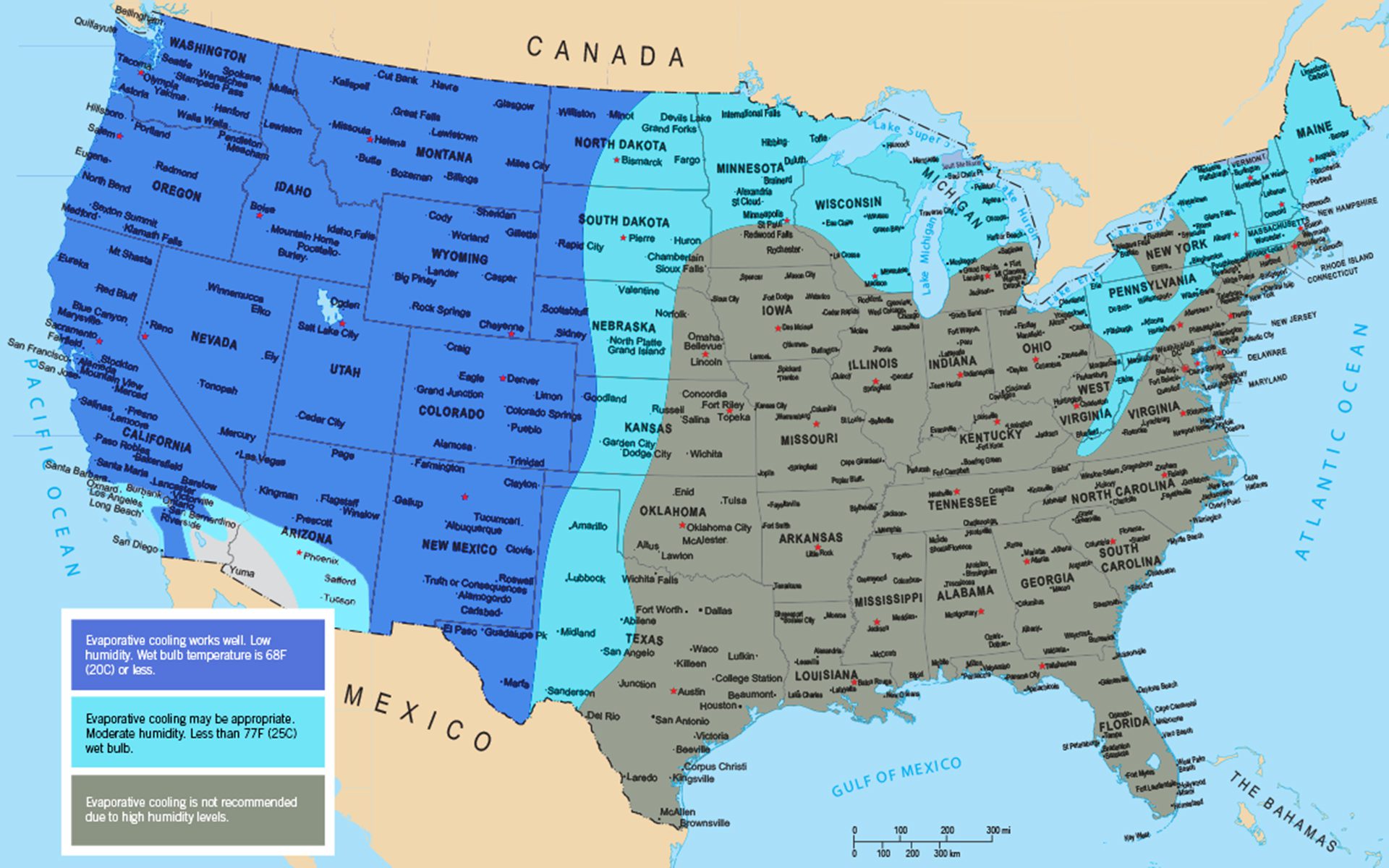
Best climate for evaporative cooling in the US
Where does evaporative cooling works best?
Evaporative cooling is most effective in dry areas of the US where the climate is hot, and humidity is low during summer. This includes the California, Nevada, New Mexico, Colorado, Utah, Arizona, Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, and specific regions in North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, and El Paso, Texas
Evaporative cooling may also work well in areas that have a combination of a cool and dry climate, and where the coincidental wet-bulb temperatures are as high as 74°F but high humidity becomes a problem no higher than the low 70s (5).
The illustrative map below provides an overview of the different climate zones for the states where evaporative cooling is more effective.
References:
- Seeley International’s calculation based on approximate running cost figures from publicly sourced data. Comparison with 1.5 star not zoned ducted refrigerative system in a large size (220m2 ) 2-star pre 2005 house in a Melbourne climate, cooling all day on the weekend and in the mornings and evenings when internal temperatures are high, and an electricity tariff of 31.9c/kWh. Negligible water cost excluded.
- This comparison is based on usage in an average-size Australian home with 4 occupants. Imperial measurements have been converted from metric.
- Based on published research articles, NATA Laboratory test results and publicly sourced data
- Psychometric chart, the relations between dry bulb, web bulb temperature and humidity
- Evaporative Cooling Systems – Climate
- The illustration is based on Office of Energy efficiency and renewable energy American Society of Heating, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) climate data and Seeley International own data analysis
- The Pacific Energy Center’s Guide to: California Climate Zones.

